The traditional password is becoming a relic. For decades, complex strings protected our data, yet 2026’s sophisticated breaches highlight their flaws.
Biometric security has emerged as the new frontier, using unique physical traits to provide protection that alphanumeric codes cannot match. This shift balances security with convenience; in a world of endless accounts, your body becomes the key.
Whether through a thumb scan or facial recognition, the barrier to your data is thinner for you but thicker for intruders. Today, this implementation is standard across sectors, from banking to entertainment platforms like Yep Casino.
Such integration ensures that only rightful owners have access to sensitive environments, reducing authentication friction while lowering account takeover risks.
By anchoring security in physical traits, developers are building a resilient digital ecosystem that prioritizes unique user identity and seamless access.
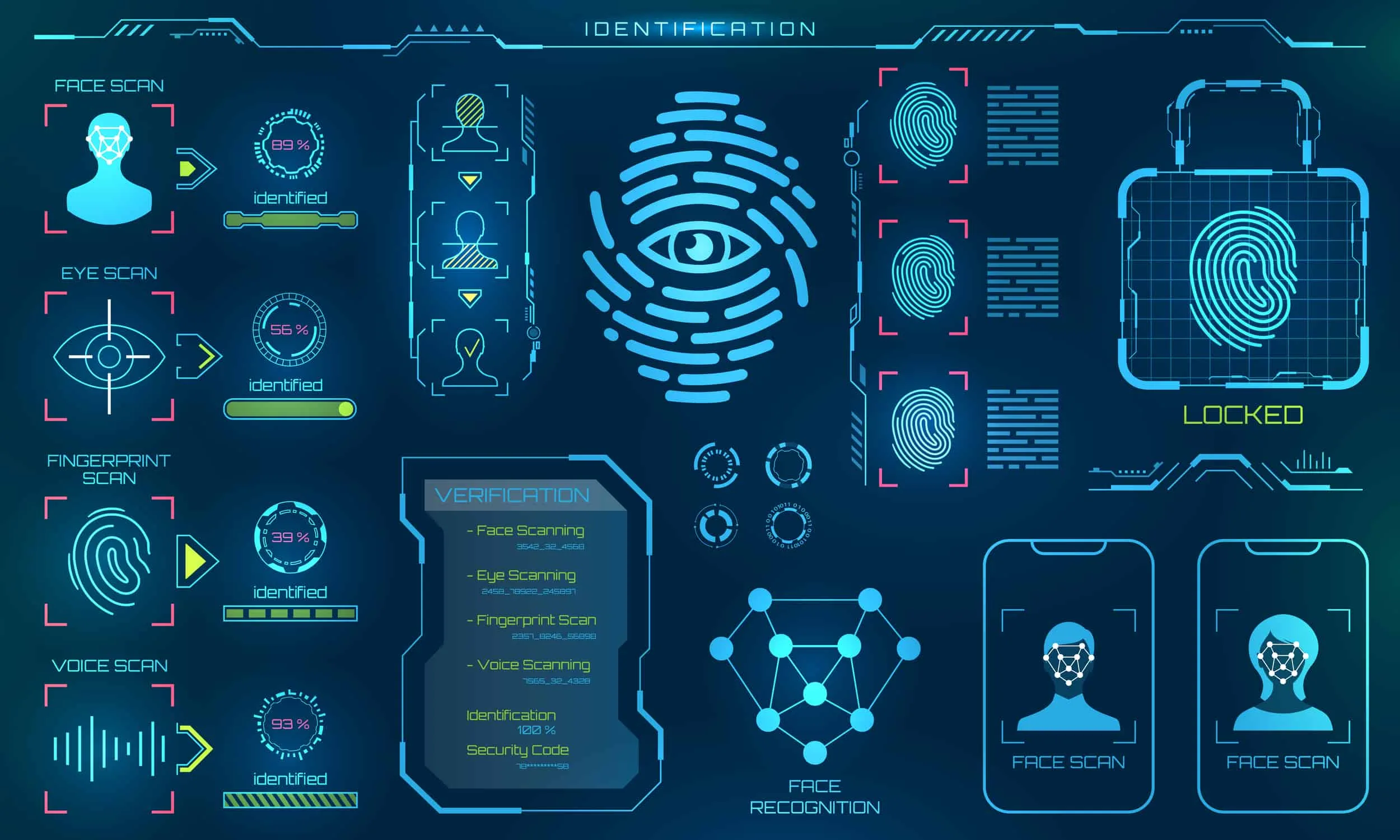
Understanding the Different Types of Biometric Authentication
Biometric security encompasses various methods to measure physical or behavioral traits, each tailored to specific devices and data sensitivity levels.
The most common forms are physiological, focusing on structures like fingerprints, facial geometry, and iris patterns.
As technology evolves, behavioral biometrics—analyzing typing speed, touchscreen pressure, or navigation patterns—are becoming increasingly prevalent. By combining these, security systems create a “multi-modal” approach that is incredibly difficult for malicious actors to spoof.
To understand how these technologies compare in terms of security and adoption, it is helpful to examine the primary categories dominating the 2026 consumer market.
| Biometric Type | Primary Focus | Best Used For | Accuracy Level |
| Fingerprint | Unique ridge patterns on digits | Mobile unlocking and payments | High |
| Facial Recognition | 3D mapping of facial features | Hands-free access and login | Moderate to High |
| Iris Scanning | Complex patterns within the eye | High-security facilities and data | Very High |
| Voice Recognition | Vocal frequency and rhythm | Customer service and smart homes | Moderate |
While each method offers a unique set of benefits, the goal remains the same: ensuring that access is granted based on who you are, rather than what you know.
This transition reduces the reliance on easily forgotten or stolen information, streamlining the user experience across all digital touchpoints.
The Advantages of Biometrics Over Traditional Passwords
The primary benefit of biometric security is the complete elimination of password fatigue. Users no longer need to manage complex codes or reuse insecure passwords across multiple platforms, thereby avoiding the risk of forgetting them.
Because biological data is inherently unique, it is significantly harder for cybercriminals to steal or guess than a standard string of text.
Furthermore, biometrics provide a much faster way to interact with digital services. In our fast-paced digital environment, the seconds saved by a quick facial or fingerprint scan encourage users to maintain active security rather than disabling it for convenience.
To maximize the effectiveness of these biological keys, modern systems often follow a specific set of protocols to ensure data remains private.
- On-Device Storage: Most smartphones store your biometric template locally in a secure hardware enclave, meaning your actual physical map is never sent to a cloud server.
- Encryption: The data is transformed into a complex mathematical representation, so even if a device is stolen, the raw biological image cannot be recovered.
- Liveness Detection: Advanced sensors can distinguish between a real human and a high-resolution photo or mask, preventing basic spoofing attempts.
These layers of protection ensure that, while your body is the key, the key itself remains entirely under your control. This localized approach to security is a significant reason why public trust in biometric systems continues to grow steadily worldwide.
Addressing Privacy and Data Concerns
Despite the clear advantages, the rise of biometrics raises valid concerns regarding privacy and the permanence of data. Unlike a password, you cannot change your fingerprint or your iris pattern if that information is ever compromised.
This makes the storage and handling of biometric information a critical priority for both developers and regulators. Ensuring that companies adhere to strict data protection laws is crucial for maintaining long-term trust with consumers.
Fortunately, the industry is moving toward decentralized identity models where users hold their own biometric proofs.
In this framework, the service provider never sees your biometric data; they only receive a confirmation that the verification was successful. This approach is a significant safeguard against large-scale database leaks.
Master Your Digital Identity Today
Biometric security represents the most significant shift in digital protection in the last twenty years. By embracing fingerprint, facial, and iris recognition, you can enjoy a more secure and convenient online experience that stays ahead of modern cyber threats.
As these technologies become more integrated into our daily routines, the era of the forgotten password will finally come to an end, replaced by a system that knows you as well as you know yourself.
Identify the accounts that support these features and activate them now to ensure your online presence remains as unique as your own signature.